Creating the world’s smallest social network (for testing purposes)
Note: I’m writing this post on my personal blog as this isn’t an official Moodle pronouncement, just some experimentation.
I’m leading Project MoodleNet, which will be “a new open social media platform for educators, focused on professional development and open content”. There are decisions I have to make, and these need to be based on criteria, prioritisation, etc.
One of the things I’m keen to do with the professional social networking component of Project MoodleNet is to ensure that it’s decentralised. By this I mean that, unlike Twitter and Facebook and Instagram, it won’t be a ‘silo’ of information.
Instead, Project MoodleNet will be federated in a way which allows information to flow between instances. It’s well explained in this article, which includes the following diagram which outlines the technical protocols on which a number of options are based:
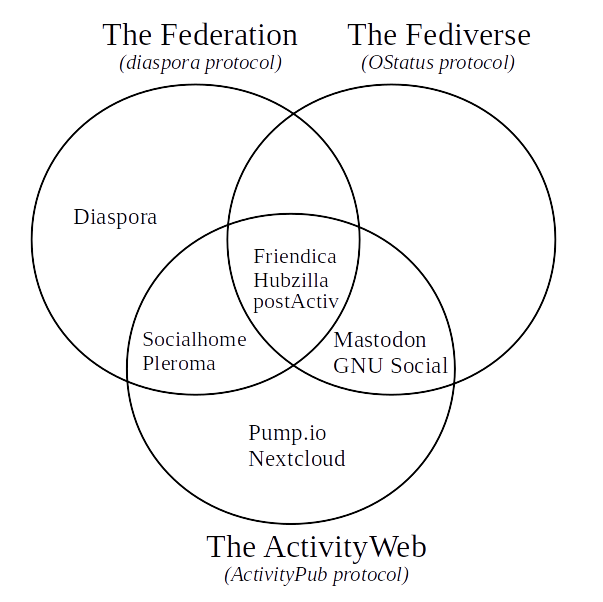
As you can see, the ActivityPub protocol is definitely a candidate for the professional social network aspect of Project MoodleNet. Last week it became a W3C recommended standard.
For less technical readers, the upshot of this is that users can send messages, files, and (most importantly) emojis to anyone on any server that uses the ActivityPub protocol. Products and services built upon this protocol may look and feel very different, but all of the data is interoperable.
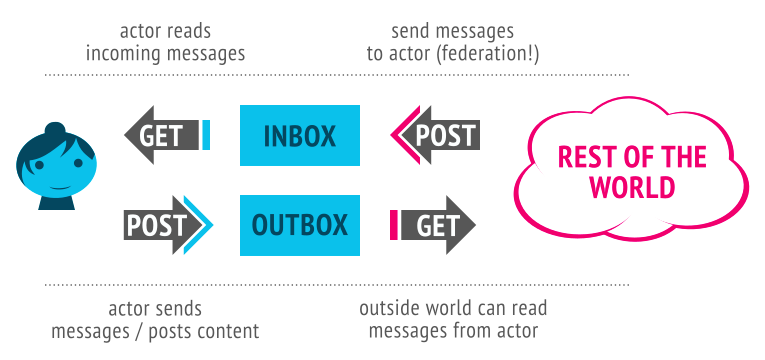
Mastodon is a social network which was originally built on the OStatus protocol, but which is now also compatible with ActivityPub. I’m a member of the social.coop instance, although there’s no limit on the number of different accounts you can hold on different instances.
Although they have a common basis, you find differences between Mastodon instances. For example, some have a particular focus, meaning that the stream of updates you get from your own instance might be focused on gaming, or education, or LGBT rights. There’s also differences between the kind of languages and content allowed by instances.
No matter which instance you’re on, however, you can follow anyone from any instance. You can see this in the screenshot below.
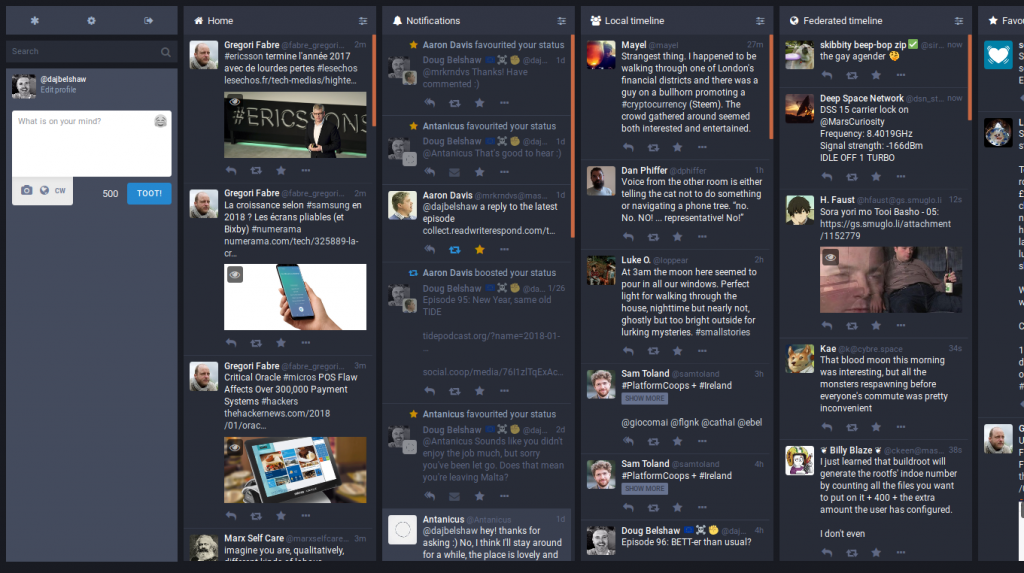
From left to right:
- My ‘Home’ stream is populated with updates from the people and accounts I follow.
- The ‘Notifications’ stream works the same as Twitter (replies, favourites, boosts)
- ‘Local timeline’ is everyone on the same instance as me.
- ‘Federated timeline’ is everyone’s updates in the Fediverse.
In practice, it’s a lot like TweetDeck (I think on purpose).
I wanted to have access to a testing version of Mastodon to look at the administration and moderation functionality. Paul Greidanus was kind enough to spin up an instance which, for obvious reasons, isn’t federated to the rest of the network.
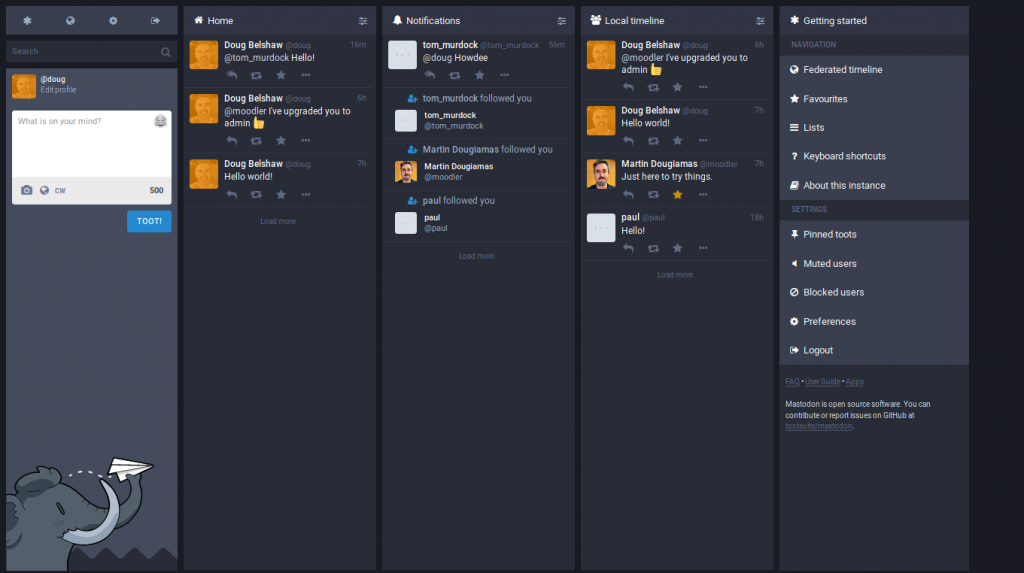
I closed self-registration and invited some Moodle staff to create an account via a special link. As you can see, it was pretty quiet. That’s OK, however, as I’m really just interested in the moderation and admin functionality.
To access the additional options available as a moderator and/or admin exist in the same place as user settings. It’s a nice touch, and the way that it’s presented makes it easy to focus on what you want to achieve, rather than getting sidetracked with technical stuff.
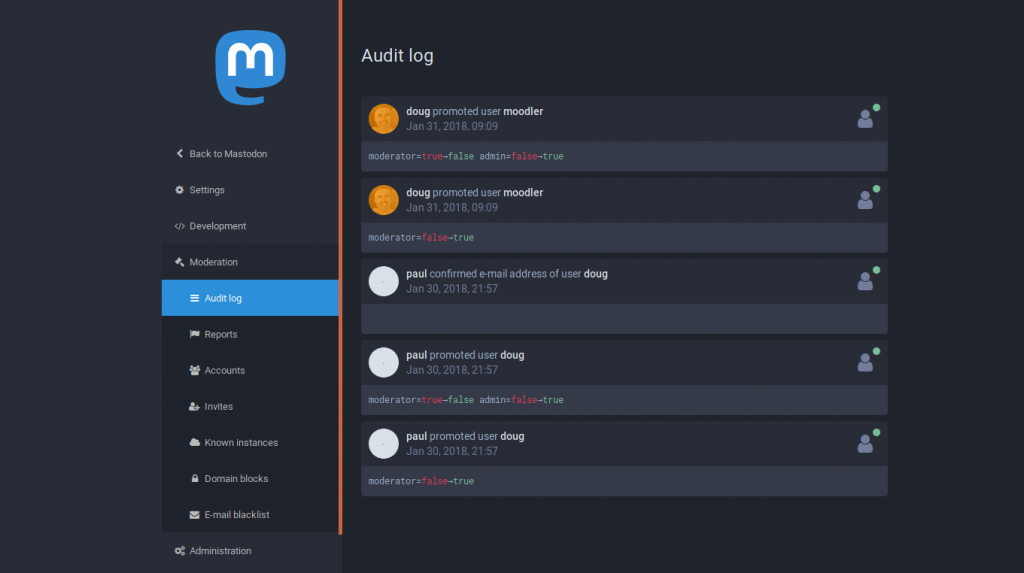
The audit log shown in the screenshot above is useful, particularly for GDPR compliance, and reporting reasons.
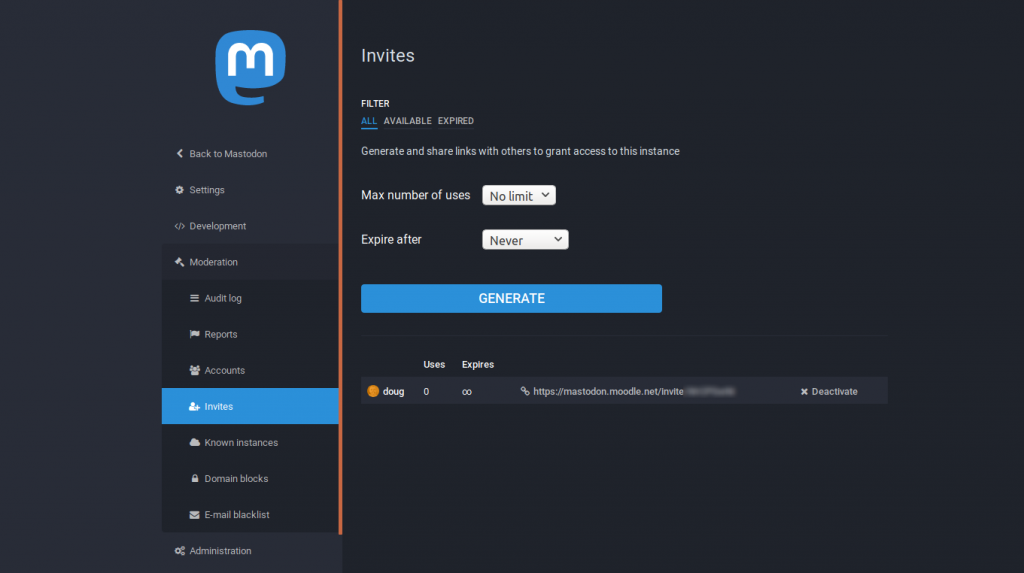
This is also the place where you can generate invitations, which can have a maximum number of uses and/or expire after a certain time. There’s also functionality around blocking email addresses from certain domains from registering.
On the admin side of things, this is where you can configure the public description of the instance, add contact details, and specify the rules and other guidelines.
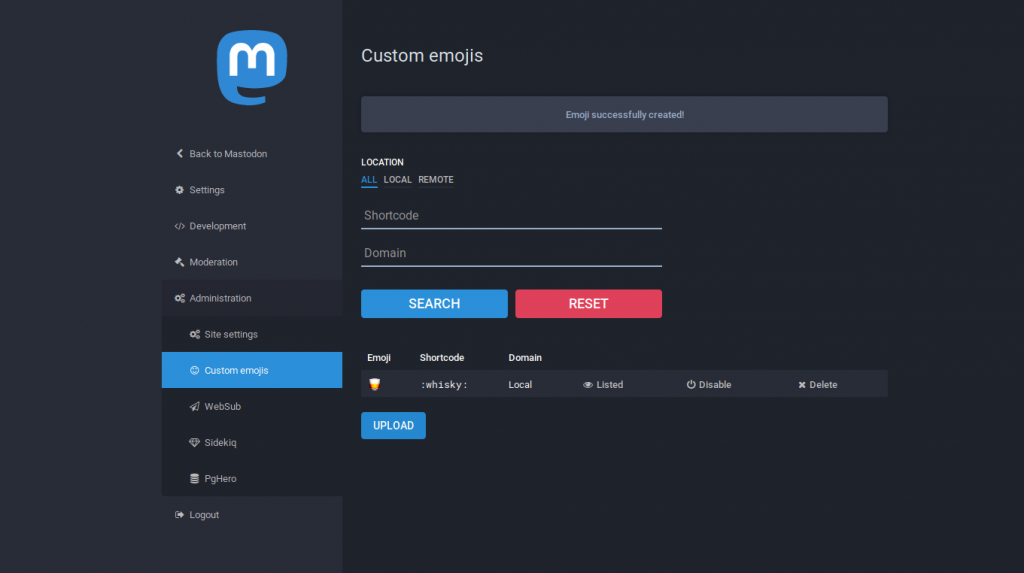
The thing that interested me most, however, was CUSTOM EMOJIS:
Finally, there’s various technical reports, and queries you can run from a technical point of view.
I have to say that I wasn’t expecting the moderation and admin side of Mastodon to be so… user-friendly. It’s incredibly easy and intuitive to use, although it does mean delving into the code if, say, you want to change the default background colour to orange!
The next thing to do is to experiment with Hubzilla, which is also mentioned on the Venn diagram earlier in this post. It’s important to experiment both technically and with users, and weigh all of these things against the principles that underpin Project MoodleNet.
Exciting times!
Main image by Slava Bowman used under a CC0 license



